Skip to content
I. Introduction
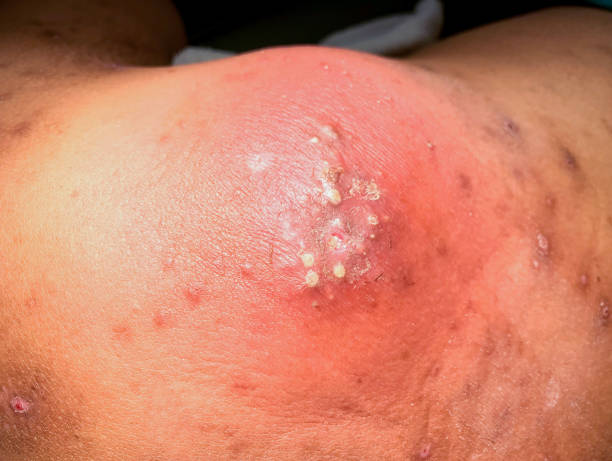
- Cellulitis: A bacterial skin infection that affects deeper layers
- Causes: Penetration of germs through cuts, scrapes, insect bites, etc.
- Common bacteria: Streptococcus and Staphylococcus
II. Symptoms of Cellulitis
- Location: Usually occurs on one side of the body
- Signs and symptoms:
- Irritated and expanding skin area
- Swelling
- Tenderness
- Pain
- Warmth
- Fever
- Chills
- Spots
- Blisters
- Skin dimpling
III. Risk Factors for Cellulitis
- Injury: Cuts, fractures, burns, and scrapes provide entry points for bacteria
- Weakened immune system: Conditions and medications that weaken immunity
- Skin conditions: Atopic dermatitis, athlete’s foot, shingles
- Chronic swelling of limbs (lymphedema)
- History of cellulitis
- Being overweight
IV. Treatment of Cellulitis
- Antibiotics: Eliminating bacterial infection with prescribed antibiotics
- Choice of antibiotics based on severity, suspected bacteria, and underlying health conditions
- Commonly prescribed antibiotics: Penicillin derivatives, cephalosporins, clindamycin
- Hospitalization may be required for intravenous (IV) antibiotic therapy in severe cases or non-responsive infections
- Self-care measures:
- Elevate the affected area to reduce swelling and improve circulation
- Apply warm compresses for pain relief and improved circulation
- Over-the-counter pain relievers for pain and inflammation
- Rest and immobilization, use of crutches or splint if necessary
- Proper wound care to prevent further infection
- Follow-up appointments to monitor progress and adjust treatment if needed
V. Prevention of Cellulitis
- Pre-emptive antibiotics for recurrent cellulitis
- Preventive actions for skin wounds:
- Daily washing with soap and water
- Consultation for protective lotions or ointments
- Regular bandaging and wound change
- Watch out for signs of infection (pain, swelling, pus)
- Special measures for individuals with diabetes or weak circulation:
- Daily foot inspection
- Regular moisturizing to prevent skin damage
- Careful trimming of nails
- Use of suitable footwear and gloves
- Prompt treatment of skin infections


