Introduction:
Acne is a common skin condition that affects people of all ages. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of acne, including its types, causes, and treatment options. By understanding the various aspects of acne, individuals can make informed decisions about managing and treating this condition effectively.
I. Types of Acne:
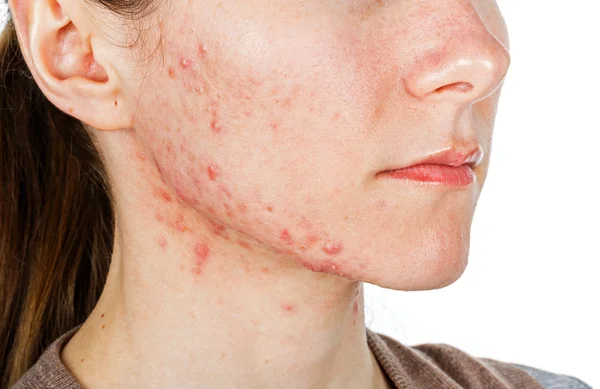
A. Whiteheads:
- Small, flesh-coloured or white bumps.
- Result from clogged pores with oil, dead skin cells, and bacteria.
B. Blackheads:
- Similar to whiteheads but with open pores.
- The dark appearance is due to oxidized melanin, not dirt.
C. Papules:
- Small, raised, red bumps.
- Tender to touch and do not contain pus.
- Caused by inflammation due to breakdown of pore walls.
D. Pustules:
- Red bumps with a yellow or white centre.
- Contain pus and are often referred to as pimples.
E. Nodules:
- Larger, solid, and painful bumps beneath the skin surface.
- Caused by a build-up of bacteria, oil, and dead skin cells.
F. Cysts:
- Large, pus-filled, painful lesions.
- Deep-rooted and can cause scarring.
- Softer to touch compared to nodules and the most severe form of acne.
II. Causes of skin breakout:
Understanding the underlying causes of acne helps in developing effective strategies for prevention and treatment. The following factors contribute to the development of acne:
A. Excess oil production:
- Sebaceous glands produce an oily substance called sebum.
- Hormonal changes can lead to overactive glands and excessive sebum production.
B. Clogged pores:
- Excess sebum mixes with dead skin cells and blocks hair follicles, forming a plug.
- Clogged pores provide a breeding ground for bacteria.
C. Bacterial activity:
- Propionibacterium acnes (P. acnes) bacteria multiply in clogged hair follicles.
- Bacterial growth triggers inflammation and the formation of lesions.
D. Hormonal factors:
- Puberty, menstrual cycles, pregnancy, and certain medical conditions can trigger or worsen acne.
- Hormonal changes affect sebum production and skin cell growth.
E. Genetic factors:
- Genetic predisposition to acne development.
- Family history of acne increases the likelihood of experiencing it.
III. Treatment Options for skin breakouts:
A. Topical treatments:
- Over-the-counter or prescription creams, gels, or lotions.
- Ingredients like benzoyl peroxide, salicylic acid, retinoids, or antibiotics.
- Reduce inflammation, unclog pores, and kill pimple-causing bacteria.
B. Oral medications:
- Antibiotics or hormonal medications prescribed by dermatologists.
- Control bacterial growth, reduce inflammation, or regulate hormone levels.
C. Isotretinoin:
- Reserved for severe, persistent condition.
- Reduces oil production, unclogs pores, and has long-lasting effects.
- Requires close monitoring due to potential side effects.
D. Procedures:
- Extraction: Manual removal of blackheads and whiteheads.
- Chemical peels: Exfoliation to unclog pores and improve skin appearance.
- Laser or light therapy: Target
Some home remedies to treat pimples:
When dealing with acne, incorporating home remedies into your skincare routine can be beneficial. Transitioning away from harsh chemicals, try these natural alternatives to soothe and manage acne-prone skin effectively:
- Firstly, cleanse your face with a gentle cleanser to remove dirt and excess oil.
- Secondly, apply a warm compress to open up the pores and promote circulation.
- Next, use tea tree oil as a spot treatment to target individual blemishes due to its antibacterial properties.
- consider using witch hazel as a toner to reduce inflammation and balance the skin’s pH levels.
- applying a honey mask can help moisturize the skin while also possessing antibacterial qualities.
- Furthermore, exfoliate with a mixture of baking soda and water to gently remove dead skin cells and unclog pores.
- The application of apple cider vinegar as a toner can help balance the skin’s acidity and reduce acne-causing bacteria.
- Additionally, incorporating aloe vera gel into your skincare routine can soothe inflammation and promote healing.
- Furthermore, consuming a well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can nourish the skin from within.
- Lastly, don’t forget to stay hydrated and maintain a consistent skincare routine to see the best results.
By transitioning to these home remedies, you can address acne concerns naturally while promoting healthier and clearer skin.

