Introduction:
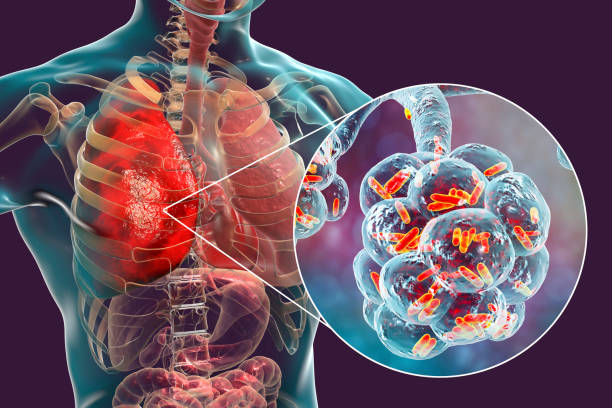
Causes of Pneumonia:
Pneumonia can be caused by a variety of factors, the most common being infectious agents. The leading causes of infectious pneumonia are bacteria and viruses. Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae, and Staphylococcus aureus are among the bacteria responsible for bacterial pneumonia. Viral pneumonia can be caused by the influenza virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and adenovirus, among others. In some cases, pneumonia can also result from exposure to certain fungi, such as Pneumocystis jirovecii, or non-infectious factors like chemical inhalation or aspiration of food or liquid.
Symptoms of Pneumonia:
The symptoms of pneumonia can vary depending on the age and overall health of the individual, as well as the specific cause of the infection. Common signs and symptoms include:
- Cough, which may produce phlegm or pus
- Chest pain, especially when breathing or coughing
- Shortness of breath or rapid breathing
- Fever, sweating, and chills
- Fatigue and weakness
- Bluish coloration of the lips and nails (indicating a lack of oxygen)
- Confusion (particularly in older adults)
Diagnosis and Treatment:
To diagnose this lung infection , a healthcare professional will typically perform a physical examination, review medical history, and order diagnostic tests. These tests may include chest X-rays, blood tests, sputum analysis, or a computed tomography (CT) scan. Once diagnosed, the treatment approach will depend on the cause and severity of the pneumonia. Bacterial pneumonia is usually treated with antibiotics, while viral pneumonia may require antiviral medications and supportive care. In severe cases, hospitalization and additional interventions, such as oxygen therapy or mechanical ventilation, may be necessary.
Prevention of Pneumonia:
Prevention involves adopting certain preventive measures. Key strategies include:
- Vaccination: Immunization against common pathogens, such as the pneumococcal vaccine and the influenza vaccine, can significantly reduce the risk of pneumonia.
- Hand hygiene: Regular handwashing with soap and water, or using alcohol-based hand sanitizers, helps prevent the spread of respiratory infections.
- Respiratory hygiene: Covering the mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow when coughing or sneezing can help prevent the transmission of respiratory droplets.
- Healthy lifestyle: Maintaining a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough rest can help strengthen the immune system, making it more resistant to infections.
- Avoiding smoking: Cigarette smoking damages the respiratory system and weakens the body’s defenses against respiratory infections.
Conclusion:
This is a significant public health concern worldwide, affecting individuals of all ages. Prompt recognition of symptoms and appropriate treatment are essential for successful recovery. While it can be serious, taking preventive measures such as vaccination, practicing good hygiene, and adopting a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk of contracting this respiratory infection. Understanding the causes, symptoms, treatment options, and prevention strategies can empower individuals to protect themselves and their loved ones from the impact of this lung infection

